|
|
synonyms: bipartite, tripartite patella
Bipartite Patella ICD-10
- Q68.2: Congenital deformity of knee
Bipartite Patella ICD-9
- 755.64 (congenital deformity of knee joint): absence of patella, genu valgum, genu varum, rudimentary patella
Bipartite Patella Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Failure of ossification of complete ossification of the patella.
- Occurs in 2-6% of the population.
- 50% will be bilateral
- Male:female = 9:1
Bipartite Patella Anatomy
- The patella is the largest sesmoid bone in the body.
- Primary ossification center appears to 4-6 years old. Secondary centers at 12 years old.
Bipartite Patella Clinical Evaluation
- Generally asymptomatic. 2% symptomatic.
- Generally men <20years old involved in sports.
- Anterior knee pain. May initially become symptomatic after an injury. Worse with squatting, climibing stairs
- May have localized tenderness on exam.
- Trauma can cause the fragment to separate through a fibrous union.
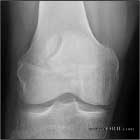
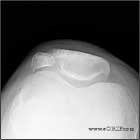
Bipartite Patella Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- Generally easily identified on plain knee films.
- If separation has occurred after trauma the space between the fragments will increase in the squatting position (get skyline view in squatting position)
- Bone scan: low specificity for symptomatic bipartite patella. 81% of asymptomatic patients will have increased uptake. (Oohashi Y, Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2007;15:1395)
- MRIL fat-suprressed T2-Weighted images may demonstrate bone marrow edema in the bipartite fragment in symptomatic patients.
Bipartite Patella Classification / Treatment
- Saupe Classification: Type I:inferior pole of the patella (5%). Type II:lateral margin (20%). Type III:superolateral pole (75%) (Saupe H, Deutshe Z Chir 1943;258:386).
- Conservative: rest, reduced sports, NSAIDs, quad stretching, dynamic patellar brace
- Surgery: Small fragments can be excised. (Bourne MK, J Pediat Orthop 1990;10: 69-73): Lateral retinacular release if non-op treatment fails. (Mori Y,Am J Sports Med 1995;23:13-18): vastus lateralis release: ORIF
Bipartite Patella Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- Patella Fracture
- nail-patella syndrome
Bipartite Patella Complications
- Patellar instability
- Incomplete relief of pain
- Nonunion
Bipartite Patella Follow-up Care
Bipartite Patella Review References
|