 |
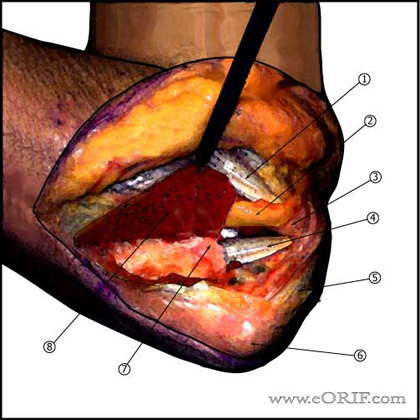
Posteromedial Approach
- Incision from 6cm proximal to olecranon to 6cm distal to olecranon. Curved around medial border of olecranon to avoid painful scar.
- Medial and lateral skin flaps are raised depending on associated pathology.
- Ulnar nerve identified and transposed anterior to the medial epicondyle.
- Flexor carpi ulnaris incised longitudinally, leaving a fascial cuff for later repair. FCU is subperiosteally elevated exposing anterior band of medial collateral ligament and the coronoid.
- Common Flexor orgin
- Transposed ulnar nerve
- Medial epicondyle
- Anterior band of medial collateral ligament
- Triceps tendon
- Olecranon
- Coronoid
- Reflected FCU origin
|
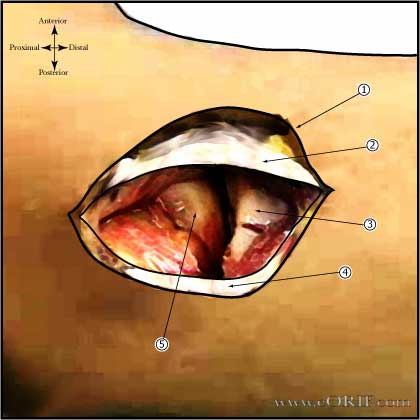 |
Kocher Lateral Approach to Radial Head
- Kocher lateral incision centered over Radial head.
- Interval between the anconeus and extensor carpi ulnaris opened. (Consider opening the white fascial layer which defines the extensor origin down to bone, going through the extensor origin, annular liagment and LCL complex as one unit.)
- ECU elevated exposing the lateral collateral ligament.
- Incise capsule anterior to the LCL complex. Exposing the radial head.
- Skin incision: Lateral incision centered over radial head.
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Radial Head
- Anconeous
- Capitellum
|
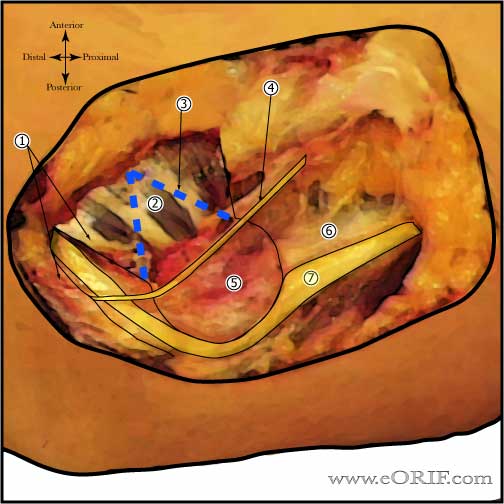 |
Ulnar Nerve Transposition Exposure
- Splint FCU exposing Ulnar nerve distally
- Common extensor origin
- Dashed blue line indicating V-incision in common extensor if performing submuscular transposition.
- Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
- Medial epicondyle
- Medial intermuscular septum: 2-3cm nust be removed before transposition
- Ulnar nerve: before transposition.
|
| |
Henry Volar Approach
- Proximal: Incision on radial aspect of volar forearm, parallel to the muscular interval between the Brachioradialis and the Pronator teres(PT)(link is external). Develop interval bluntly down to the lacertus fibrosis.
- Useful for: Distal Biceps Repair,
|





