 |
synonyms:
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome ICD-10
- I74.2: Embolism and thrombosis of arteries of the upper extremities
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome ICD-9
- 444.21 Arterial embolism and thrombosis; upper extremity
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Etiology / Epidemiology / Natural History
- Thrombosis of the ulnar artery in Guyon's canal, resulting from blunt or repetitive trauma to the base of the hypothenar eminence.
- Repetitive trauma may lead to formation of a pseudoaneursym or ulnar artery thrombosis.
- Most common upper extremity arterial occlusion.
- Males > females
- Associated with smokingand fibromuscular dysplasia
- May occur in baseball catchers or golfers.
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Anatomy
- 22% of patients have an incomplete superficial palmar arch, 3% have imcomplete deep palmar arch.
- mixed=proximal, motor only=hook of hamate, pure sensory=distal to hamate
- roof=volar carpal ligament. Floor=transverse carpal ligament & pisohamate ligament. Ulnar wall=hook of hamate. Radial wall =pisiform &ADM muscle muscle.
- sources=ganglia(85%)(MRI), hook of hamate nonunion(CT), ulnar artery thrombosis(U/S), anomalous muscle, palmaris brevis hypertrophy
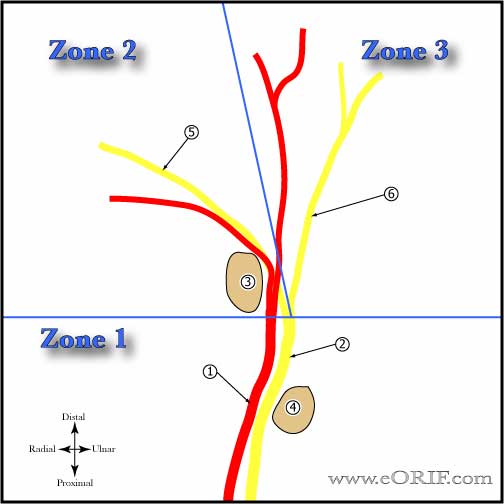
- Ulnar tunnel zone 1=proximal to bifurcation of nerve associated with mixed motor/sensory. Most common lesions = ganglions and hook of hamate fracture.
- Ulnar tunnel zone 2=hook of hamate, deep motor branch only. Most common lesions = ganglions and hook of hamate fracture.
- ulnar tunnel zone 3=superficial sensory branch only. Most common lesions = Ulnar artery thrombosis.
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Clinical Evaluation
- Ulnar nerve symptoms: numbness, tingling, pain, weakness
- Ischemic symptoms: cold intolerance, pain, occasionally ulceration of the small and/or ring finger or even gangrene.
- Allen's test is positive.
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Xray / Diagnositc Tests
- P/A and lateral views of the wrist typically normal.
- Doppler ultrasonography confirms diagnosis.
- EMG/NCVconsider for patients with ulnar nerve symptoms.
- MRI: consider to evaluate for space occupying lesions
- CTscan: best test to evaluate for hook of hamate fracture.
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Classification / Treatment
- Acute: consider urokinase, streptokinase thrombolysis.
- Conservative: smoking cessation, activity modification, calcium channel blockers, alpha blockers, beta blockers, steriods, intravenous prostaglandin, heparin.
- Treatment = excision of the thrombosis segment with reconstruction using reversed vein graft. Reocclusion or aneurysm is not uncommon. Other options = endarterectomy, thrombus excision with ligation of artery.
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Associated Injuries / Differential Diagnosis
- Ulnar artery thrombosis = Hypothenar hammer syndrome
- Flexor tendonitis
- TFCC tear
- Hook of the Hamate fracture
- Wartenberg's Syndrome
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome(commonly coexist, release of transverse carpal ligament adequetely decompresses Guyons canal)
- Autoimmune vasculitis
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Emboli
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Complications
- Failure/ reocclusion
- Persistent numbness
- Palmar hypersensitivity
- Distal Ulnar nerve palsy (motor branch)
- Wound dehiscence
- Infection
- Gangrene
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Follow-up Care
- Post-op: Volar splint, NWB
- 7-10 Days: Remove sutures, consider night time splinting. Start gentle ROM exercises
- 6 Weeks: Begin strengthening exercises
- 3 Months:Return to full activities / sport
Hyothenar Hammer Syndrome Review References
|