|

|
synonyms:Hip IMHS, intramedullary hip screw, gamma nail, trigen intertan nail
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS CPT
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Anatomy
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Indications
- Unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures
- Subtrochanteric hip fractures
- Reverse obliquity intertrochanteric hip fractures
- Impending / pathologic proximal femur fracture
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Contraindications
- Femoral neck fracture
- Hip anklyosis
- Femoral shaft deformity
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Alternatives
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Pre-op Planning
- Smith & Nephew Trigen Intertan (provides solid fixation in the head, more time consuming)
- Stryker Gamma Nail (less fixation in the head, less time consuming)
- Biomet Peritrochanteric Nail (PTN)
- Consider subfascial transexamic acid injection to reduce peri-operative transfusion requirements by 43%. (Drakos A, JOT 2016, 30:409)
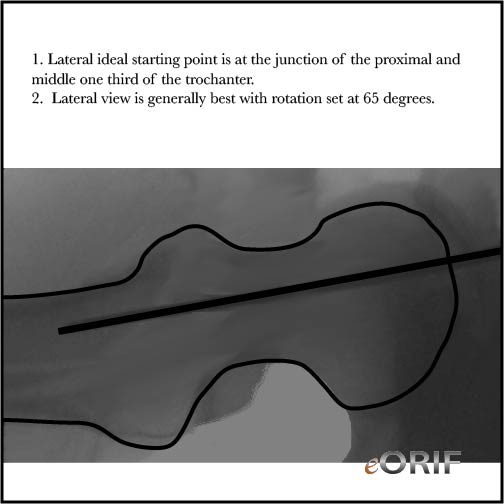
- Fluoro tips: AP image with machine approximately 15-20° over the top of the patient generally demonstrates the outline of the greater trochanter, and aids in visualization of the starting point for the nail. Lateral view is generally best with rotation set around 65 degrees.
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture Reduction Techniques
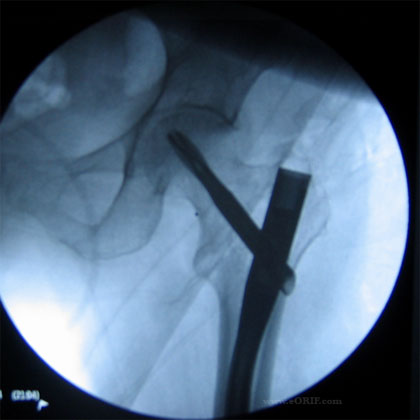
- Ensure guide pin is placed into bone on the trochanter. Must ensure bone is removed to allow room for nail or the nail with displace the fracture when inserted.
- Apex anterior angulation on lateral view: use ball spike placed through anterior stab incision to push femoral neck.
- Valgus angulation: place bone hook around neck to gain reduction.
-
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Technique
- Sign operative site.
- Pre-operative antibiotics, +/- regional block.
- General endotracheal anesthesia
- Supine position on Hana table. All bony prominences well padded.
- Prep and drape in standard sterile fashion.
- Reduce fracture using
- Irrigate.
- Close in layers.
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Complications
- Screw cut-out: associated with tip-apex distance >25mm, increasing age of the patient, an unstable fracture, a poor reduction, & use of a high-angle (150deg) side-plate
- Loss of fixation
- Osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- Femoral shaft fracture
- Nonuion
- Infection
- Nerve or vascular injury
- Painful hardware
- Compartment Syndrome
- CRPS
- DVT / PE
- Heterotopic Ossification
- Infection, nerve or artery damage, stiffness, weakness, incomplete relief of pain, incomplete return of function or motion, incomplete return to sport, need for further surgery. Medical complications including heart attack, stroke, blood clots, pulmonary embolus, transfusion reaction or death.
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Follow-up care
- Post-op:Consider DVT prophylaxis. Weight-bearing as tolerated. Typically require short-term rehabilitation. Osteoporosis evaluation is generally indicated.
- 7-10 Days:
- 6 Weeks:
- 3 Months:
- 6 Months:
- 1Yr:
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Outcomes
Intertrochanteric Hip Fracture IMHS Review References
|