 |
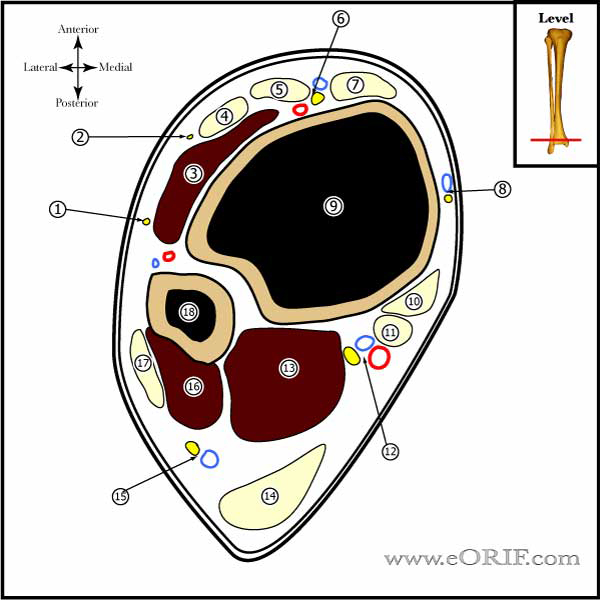
See Ankle Cross Sections |
| ROM Dorsiflexion = 20 degrees Plantarflexion = 50 degrees |
|
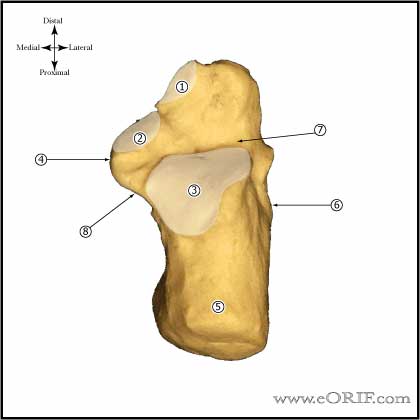 |
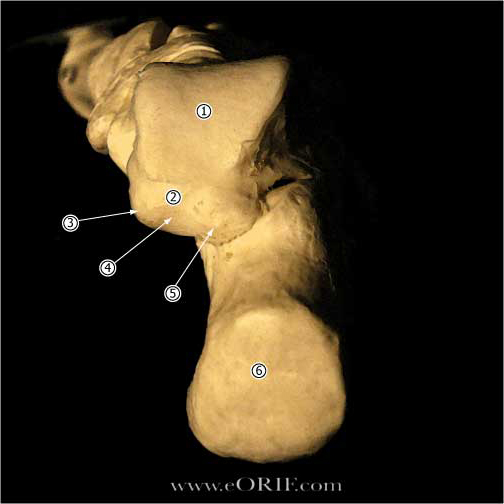
Calcaneous Anatomy |
| Talus Anterior portion of the talar dome is @2.4mm wider than the posterior portion, making the ankle much more stable in dorsiflexion than in plantarflexion. |
|
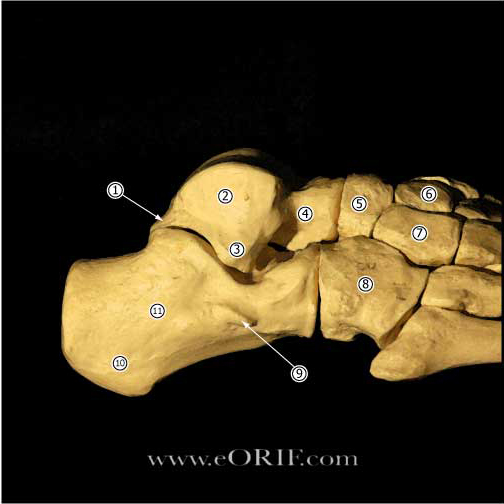
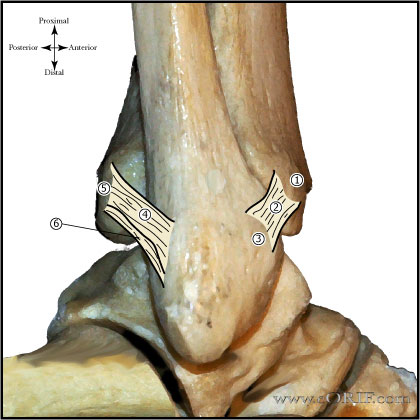
| Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) (Burks RT, AJSM 1994;22:72) Orign: anterior aspect of the distal fibula 1 cm from the tip of the lateral malleolus. Insertion: lateral aspect of the talar neck just distal to the articular surface 18 mm proximal to the subtalar joint. 7.2mm width, @12mm length (Ruth C, JBJS 1961;43A:229) Strain increases when the ankle moves into greater degrees of plantar flexion, internal rotation, and inversion (Colville MR, AJSM 1990;18A;196) Primary restraint to inversion in plantar flexion. Also resists anterolateral translation of the talus in the mortise. |
|
| Calcaneofibular Ligament (CFL) (Burks RT, AJSM 1994;22:72) Origin: distal tip of fibula adjacent to the ATFL, 8 mm proximal to the tip Insertion: lateral wall of calcaneous, 13 mm distal to the subtalar joint, deep to the peroneal tendon sheaths. 4-6mm in diameter (Ruth C, JBJS 1961;43A:229) Angled 133 degrees (range, 113 to 150 degrees) in relation to the fibula with the ankle in plantigrade position. Strain increases when the talus is dorsiflexed and inverted. (Colville MR, AJSM 1990;18A;196) Primary restraint to inversion when the ankle is in neutral or dorsiflexion. Limits talar tilt. |
|
| Posterior Talofibular Ligament (PTFL) Origin: posterior border of the fibula Insertion: posterior lateral talus 6mm diameter, 9mm length (Ruth C, JBJS 1961;43A:229) |
|
| Lateral Talocalcaneal Ligament (LTCL) Origin: lateral body of talus Insertion: lateral calcaneous variable size, often ill defined Funtion: limits subtalar motion. |
|
 |
Posteroinferior Tibiofibular Ligament |
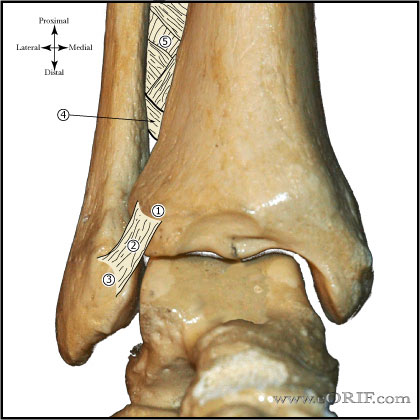 |
Anteroinferior Tibiofibular Ligament Origin: anterolateral (Chaput’s) tubercle of the tibia. Insertion: anterior (Wagstaffe’s) tubercle of the fibula Funtion: Important in adolescent transitional ankle fracture configuration. |
| Inferior Transvere Ligament Origin: posterior lateral malleolus Insertion: posterior distal tibia Funtion: extention of the articular surface of the talus. |
|
| Deltoid Ligament Has superficial and deep portions. Superificial: tibionavicular, calcaneofibular and posterior talotibial ligaments. Deep: anterior talotibial ligament. Funtion: |
|
| Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis consists of: AITFL, IOL, interosseous membrane, PITFL, and ITL. |
|
| IOL (interosseous ligament) thickened distal part of the interosseous membrane. |
|
| Sural Nerve sensory nerve formed by the medial sural nerve (branch of the tibial nerve) and lateral sural nerve(branch of the common peroneal nerve). Courses between the heads of the gastrocnemius, eventually emerging though the gastrocs fascial covering. Travels in the superfical posterior compartment of the leg. It crosses near the midline at the level of the musculotendinous junction of the achilles (@9.8 cm from the calcaneus) before descending to its more lateral location distally. At the level of insertion of the Achilles into the calcaneus, the sural nerve is 18.8 mm from the lateral border of the Achilles tendon. (Webb J, Foot ankle Int 2000;21:475). The sural nerve supplies lateral calcaneal branches to the heel, then descends 1-1.5 cm behind the lateral malleolus, anterolateral to the short saphenous vein suppling sensation to the lateral malleolus, Achilles tendon, and the ankle joint. The sural nerve continues on the lateral aspect of the foot supplying sensation to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, fourth interosseous space, and the fifth toe. Can be injured during surgery for Achilles tendon rupture. Injected during ankle block. Travels with the Lesser Saphenous during much of its course in the leg. |
|
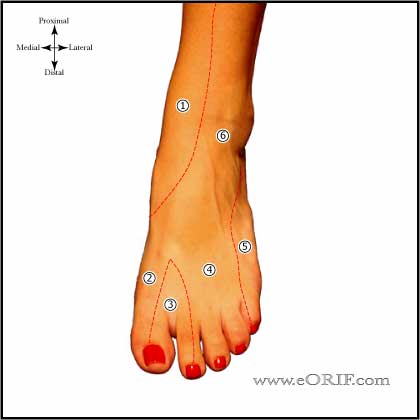 |
Superficial Peroneal Nerve innervates dorsolateral foot. |
| Lateral Calcaneal Nerve Branch of sural nerve Runs along the lateral border of the Achilles tendon Innvervates the lateral heal pad. May be injured during posterior portal placement during Ankle Arthroscopy (Sitler DF, JBJS 2002;84A:763). |
|
| Distal Tibial Ossification Distal tibial ossification center appears at 6-24 months old. Closes at 15 in girls, and 17 in boys Medial malleolar ossification center appears at 7 years old, closes at 10yrs old. |
|
| Distal Fibular Ossification Ossification center appears at 9-24 months. Closes around 16 in girls and 18 in boys. |