|
|
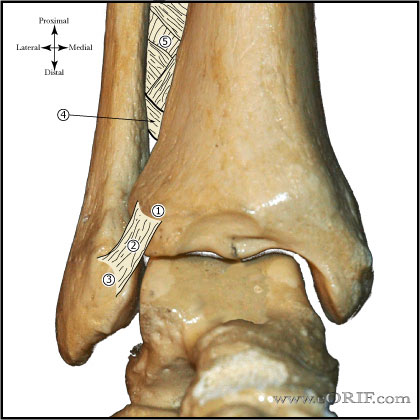
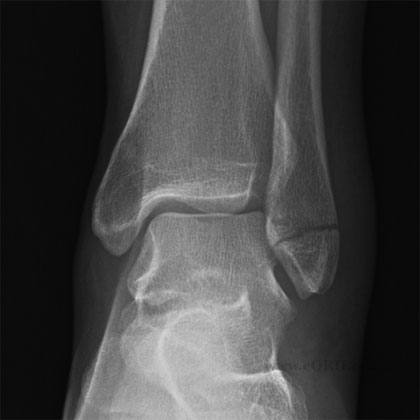
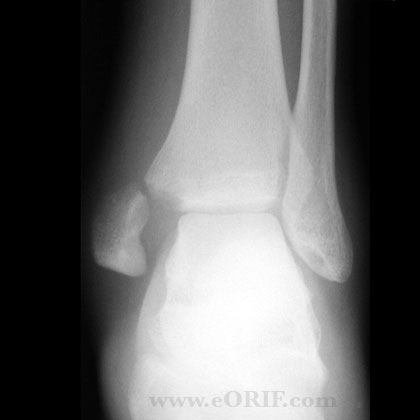
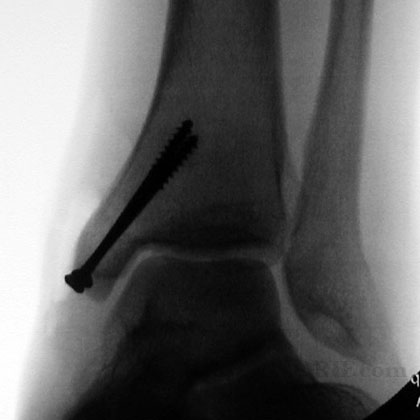
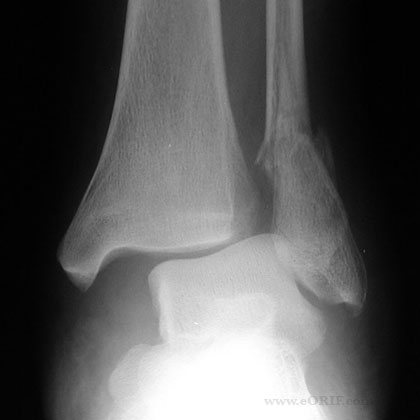
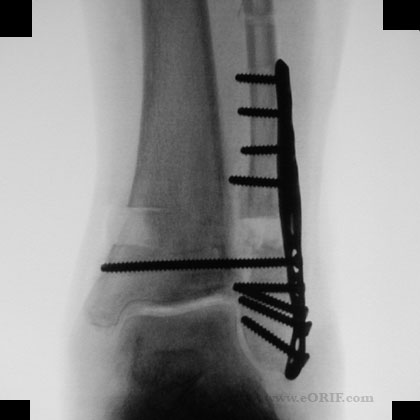
synonyms: ORIF Ankle Fracture, open reduction internal fixation ankle, medial malleolus ORIF, lateral malleolus ORIF
ORIF Ankle Fracture Indications
ORIF Ankle Fracture Contraindications
ORIF Ankle Fracture Alternatives
ORIF Ankle Fracture Pre-op Planning / Special Considerations
ORIF Ankle Fracture Complications
ORIF Ankle Fracture Follow-up care
ORIF Ankle Fracture Review References
|